 FreeLong++
Training‑Free Long Video Generation via Multi‑band SpectralFusion
FreeLong++
Training‑Free Long Video Generation via Multi‑band SpectralFusion
Abstract
Recent advances in video generation models have enabled high‑quality short video generation from text prompts. However, extending these models to longer videos remains a significant challenge, primarily due to degraded temporal consistency and visual fidelity. Our preliminary observations show that naively applying short‑video generation models to longer sequences leads to noticeable quality degradation. Further analysis identifies a systematic trend where high‑frequency components become increasingly distorted as video length grows—an issue we term high‑frequency distortion. To address this, we propose FreeLong, a training‑free framework designed to balance the frequency distribution of long‑video features during the denoising process. FreeLong achieves this by blending global low‑frequency features, which capture holistic semantics across the full video, with local high‑frequency features extracted from short temporal windows to preserve fine details. Building on this, FreeLong++ extends FreeLong's dual‑branch design into a multi‑branch architecture with multiple attention branches, each operating at a distinct temporal scale. By arranging multiple window sizes from global to local, FreeLong++ enables multi‑band frequency fusion from low to high frequencies, ensuring both semantic continuity and fine‑grained motion dynamics across longer video sequences. Without any additional training, FreeLong++ can be plugged into existing video generation models (e.g., Wan2.1 and LTX‑Video) to produce longer videos with substantially improved temporal consistency and visual fidelity. We demonstrate that our approach outperforms previous methods on longer‑video generation tasks (e.g., 4× and 8× the native length). It also supports coherent multi‑prompt video generation with smooth scene transitions and enables controllable video generation using long depth or pose sequences.
FreeLong++ Framework
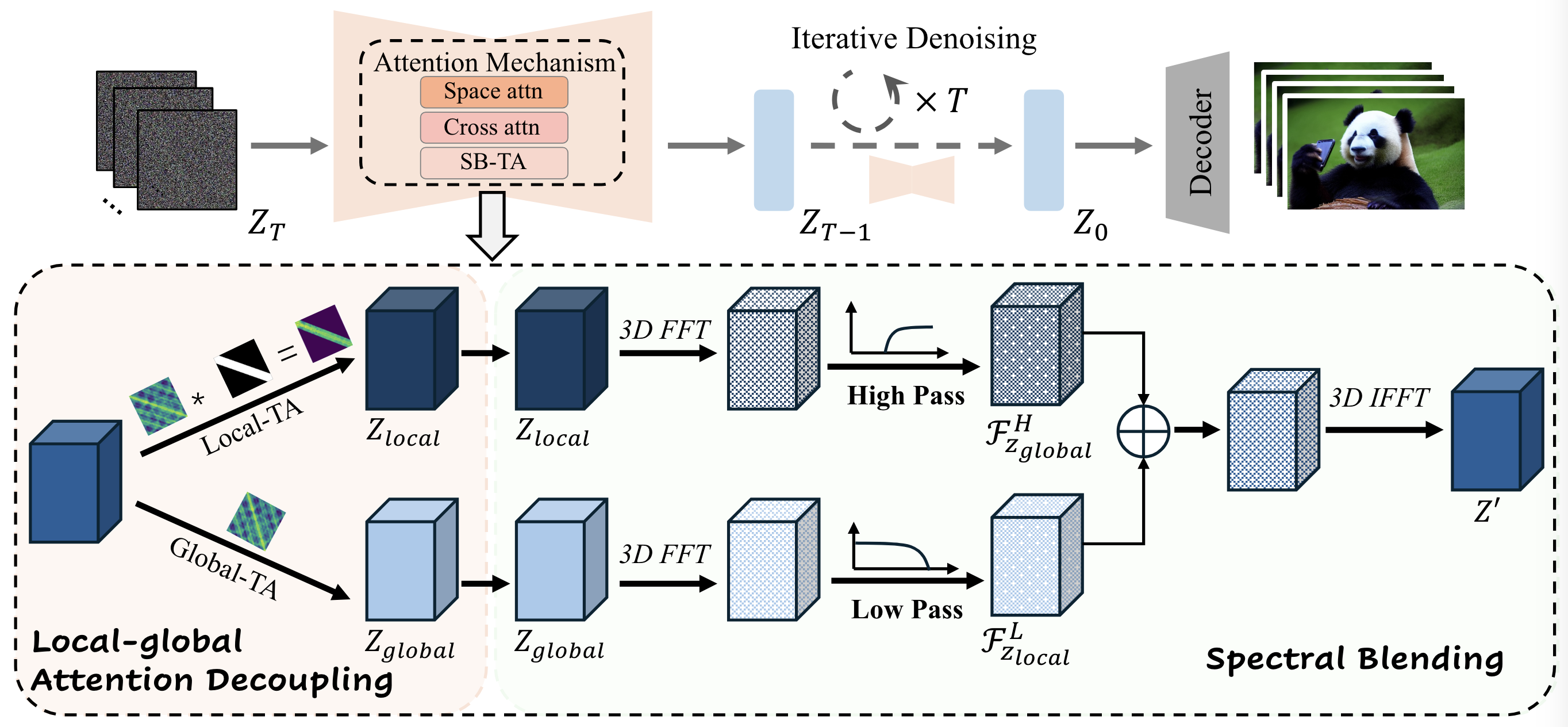
The FreeLong++ framework extends FreeLong by introducing Multi‑band SpectralFusion Attention. Multi‑scale temporal branches with varying window sizes capture motion dynamics at different frequency bands. Each branch is processed in the frequency domain and selectively fused via scale‑specific filters, enhancing long‑range consistency while preserving fine‑grained motion.
Long videos generated before and after FreeLong++.
Comparison with Other Methods.
Multi‑Prompt Videos.
Long‑Control Videos.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{lufreelong,
title={FreeLong: Training-Free Long Video Generation with SpectralBlend Temporal Attention},
author={Lu, Yu and Liang, Yuanzhi and Zhu, Linchao and Yang, Yi},
booktitle={The Thirty-eighth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems}
}
@article{lu2025freelongpp,
title={FreeLong++: Training-Free Long Video Generation via Multi-band SpectralFusion},
author={Yu Lu and Yi Yang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2507.00162},
year={2025},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.00162}
}